The major players in the foreign exchange market are a diverse group of institutions and individuals who play a vital role in the global financial system. These players include central banks, commercial banks, investment banks, hedge funds, and retail traders. Each type of participant has a unique role to play in the market, and their interactions with each other help to determine the overall direction of currency prices.
Central banks are the most important players in the foreign exchange market. They are responsible for managing their country's monetary policy, which includes setting interest rates and intervening in the currency market to influence the value of their currency. Commercial banks are the largest participants in the foreign exchange market. They provide foreign exchange services to their customers, such as currency exchange and international wire transfers. Investment banks are also major players in the foreign exchange market. They trade currencies on behalf of their clients and provide advisory services to corporations and governments.
Market Participants
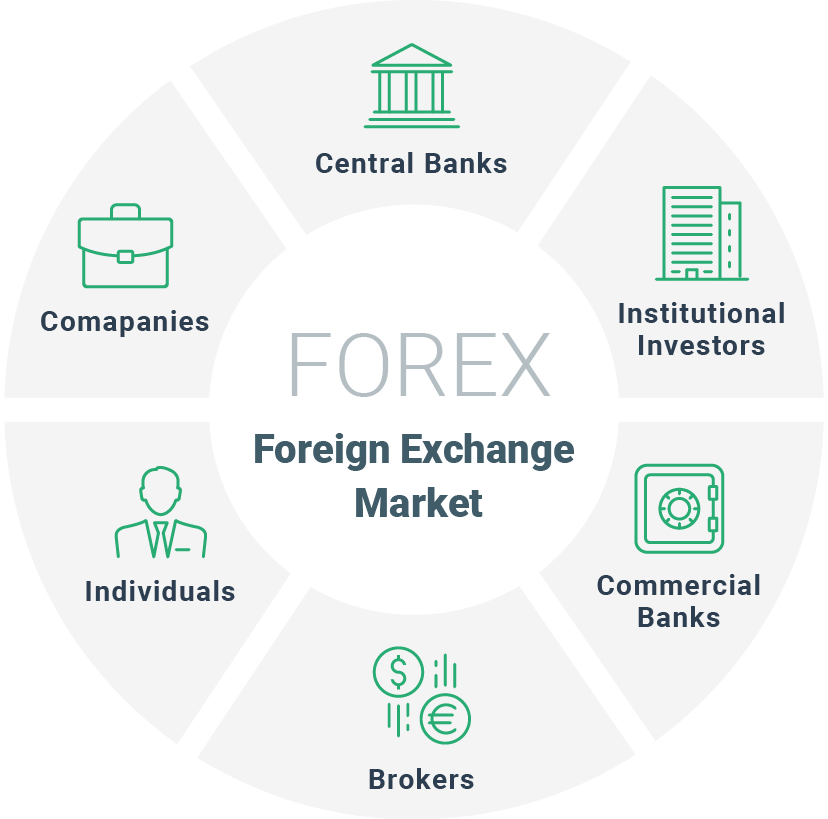
The foreign exchange market is a vast and complex global marketplace where currencies are traded. A wide range of participants, from individuals to large financial institutions, engage in foreign exchange transactions for various reasons.
The major participants in the foreign exchange market can be categorized into the following groups:
Central Banks
- Central banks are responsible for managing a country's monetary policy and regulating its financial system.
- They participate in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currency, manage foreign exchange reserves, and facilitate international trade.
- Examples: Federal Reserve (United States), Bank of England (United Kingdom), European Central Bank (Eurozone)
Commercial Banks
- Commercial banks facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their customers, such as businesses and individuals.
- They provide foreign exchange services, including currency exchange, wire transfers, and trade finance.
- Examples: Citibank, HSBC, JPMorgan Chase
Investment Funds
- Investment funds, such as hedge funds and mutual funds, participate in the foreign exchange market to generate profits through currency trading.
- They use various investment strategies, including carry trade, momentum trading, and currency arbitrage.
- Examples: Bridgewater Associates, Renaissance Technologies, BlackRock
Corporations
- Corporations engage in foreign exchange transactions to facilitate international trade and manage their foreign currency exposure.
- They buy and sell currencies to settle payments, hedge against currency fluctuations, and raise capital in foreign markets.
- Examples: Apple, Toyota, Volkswagen
Retail Traders
- Retail traders, including individuals and small businesses, participate in the foreign exchange market to speculate on currency movements.
- They use online trading platforms to buy and sell currencies in small amounts.
- Examples: Individual traders using MetaTrader, eToro, Coinbase
Market Structure: The Major Players In The Foreign Exchange Market Are
The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. The market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and it is traded in a variety of different locations around the world.
The foreign exchange market is organized into a network of banks, brokers, and other financial institutions. These institutions act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of currencies, and they facilitate the execution of foreign exchange transactions.
Types of Transactions
The most common type of foreign exchange transaction is a spot transaction. A spot transaction is a transaction that is settled on the spot, meaning that the currencies are exchanged immediately. Other types of foreign exchange transactions include forward transactions, which are transactions that are settled at a future date, and swap transactions, which are transactions that involve the exchange of two different currencies at two different future dates.
Further details about foreign exchange market deals in is accessible to provide you additional insights.
Market Instruments
The foreign exchange market facilitates trading in a diverse range of financial instruments, each with unique characteristics and uses. These instruments can be broadly categorized into spot instruments, forwards, futures, options, and swaps.Spot Instruments
Spot instruments involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. Transactions are typically settled within two business days. Spot instruments are commonly used for immediate settlement of international trade obligations or for short-term speculative trading.Forwards
Forwards are customized contracts that obligate the buyer and seller to exchange a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date. Forwards are primarily used for hedging against exchange rate fluctuations over a specific time horizon.Futures
Futures are standardized exchange-traded contracts that require the buyer and seller to exchange a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a specific future date. Futures provide a transparent and liquid market for hedging and speculative trading.Options
Options grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified amount of currency at a predetermined exchange rate on or before a specific future date. Options provide flexibility and allow traders to manage risk or speculate on future exchange rate movements.Swaps
Swaps involve the exchange of cash flows denominated in different currencies over a specified period. Swaps are commonly used for managing interest rate risk, currency risk, and for speculative trading.Market Regulation
The foreign exchange market is a highly regulated market, with a complex regulatory framework in place to ensure its stability and integrity. This framework includes a combination of national and international regulations, as well as self-regulatory initiatives.
For descriptions on additional topics like foreign exchange market spot and forward, please visit the available foreign exchange market spot and forward.
The regulatory framework for the foreign exchange market is designed to achieve several objectives, including:
- Preventing and detecting market abuse, such as insider trading and market manipulation.
- Ensuring the orderly functioning of the market, including by setting trading rules and standards.
- Protecting the interests of market participants, including retail investors and institutional investors.
Regulatory Bodies
The foreign exchange market is overseen by a number of regulatory bodies, including:
- The Bank for International Settlements (BIS): The BIS is an international organization that promotes cooperation among central banks and other financial institutions. It plays a key role in setting global standards for the foreign exchange market, including the Basel Accords.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF): The IMF is an international organization that provides financial assistance to countries in need. It also plays a role in promoting financial stability and overseeing the global financial system.
- The Financial Stability Board (FSB): The FSB is an international body that coordinates financial regulation and supervision. It plays a key role in identifying and addressing risks to the global financial system.
- National regulatory authorities: National regulatory authorities, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), are responsible for regulating the foreign exchange market within their respective jurisdictions.
Impact of Regulation
Regulation has a significant impact on the foreign exchange market. It helps to ensure the market is fair, orderly, and transparent. It also helps to protect market participants from abuse and exploitation.
In this topic, you find that foreign exchange rate adalah is very useful.
However, regulation can also have some negative consequences. It can increase the cost of doing business in the foreign exchange market, and it can make it more difficult for new entrants to enter the market.
Overall, the regulatory framework for the foreign exchange market is essential for ensuring its stability and integrity. It helps to protect market participants and promote fair and orderly trading.
Market Trends

The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, shaped by a variety of factors. These trends are driven by economic, political, and technological developments, and they have a significant impact on the market's structure, instruments, and participants.
Factors Driving Market Trends, The major players in the foreign exchange market are
- Globalization: Increased global trade and investment have led to a greater demand for foreign currencies.
- Technological advancements: Electronic trading platforms and mobile apps have made it easier for individuals and businesses to participate in the forex market.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in emerging markets has attracted foreign investment and increased the demand for their currencies.
- Political instability: Political events, such as elections, wars, and trade disputes, can have a significant impact on currency values.
- Monetary policy: Interest rate changes and other monetary policy decisions by central banks can influence the value of currencies.
Potential Impact of Market Trends
- Increased volatility: Globalization and technological advancements have made the forex market more volatile, creating both opportunities and risks for traders.
- Greater participation: Electronic trading platforms have lowered barriers to entry, allowing more individuals and businesses to participate in the market.
- Shift in market dynamics: The rise of emerging markets has shifted the balance of power in the forex market, with currencies from these countries playing a more significant role.
- Increased regulatory scrutiny: As the forex market has grown, regulators have increased their scrutiny to ensure fair and orderly trading.
Market Outlook
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, and the outlook for the future is always uncertain. However, there are a number of factors that are likely to affect the market in the coming years.
One of the most important factors is the global economy. The strength of the global economy will have a major impact on the demand for foreign exchange, as well as the value of currencies.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are another important factor that will affect the foreign exchange market. Changes in interest rates can make one currency more or less attractive to investors, which can lead to changes in its value.
Political Risk
Political risk is another factor that can affect the foreign exchange market. Political instability in a country can lead to a decrease in the value of its currency, as investors become less willing to invest in that country.
Recommendations for Investors
Given the uncertainty of the foreign exchange market, it is important for investors to be aware of the risks involved. Investors should also diversify their portfolios and invest in a variety of currencies to reduce their risk.
Closing Summary

The foreign exchange market is a complex and ever-changing environment. The major players in the market are constantly adapting to new conditions, and their interactions with each other help to shape the overall direction of currency prices. By understanding the roles of the different participants in the foreign exchange market, we can gain a better understanding of how the market works and how to make informed decisions about currency trading.
