In the ever-evolving realm of global finance, the conclusion for foreign exchange market project stands as a pivotal juncture, where an in-depth examination of the forces shaping currency exchange rates unveils actionable insights for traders, investors, and businesses alike.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the foreign exchange market, empowering readers to navigate its complexities with confidence and precision.
Foreign Exchange Market Overview

The foreign exchange (forex) market is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
The forex market plays a vital role in facilitating international trade and investment. It allows businesses and individuals to exchange currencies to settle transactions and manage their foreign exchange risk.
Major Participants in the Forex Market
- Commercial banks are the largest participants in the forex market. They provide foreign exchange services to their customers, including currency exchange, hedging, and international payments.
- Investment banks are also major players in the forex market. They trade currencies for their own accounts and for their clients.
- Central banks intervene in the forex market to influence the value of their currencies.
- Retail traders are individuals who trade currencies on a smaller scale.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions
- Spot transactions are the most common type of forex transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate.
- Forward transactions are contracts to exchange currencies at a specified rate on a future date.
- Currency swaps are agreements to exchange currencies and then swap them back at a later date.
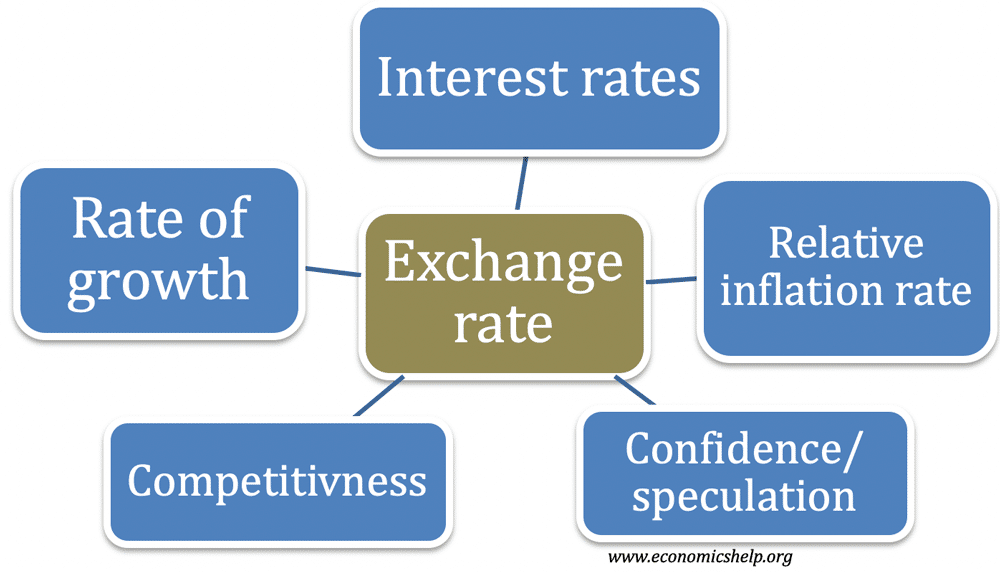
Factors Influencing Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are influenced by a complex interplay of economic and political factors, as well as the forces of supply and demand. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers.
Economic Factors
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in a country typically leads to a higher demand for its currency, causing its value to appreciate.
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less desirable and causing its value to depreciate.
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to foreign investors, increasing demand and causing its value to appreciate.
- Trade balance: A country with a positive trade balance (exports exceeding imports) experiences an increased demand for its currency.
Political Factors
- Political stability: Political uncertainty and instability can lead to currency depreciation as investors lose confidence.
- Government policies: Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can impact currency values. li>International relations: Diplomatic tensions and conflicts can affect currency exchange rates.
Supply and Demand
The value of a currency is determined by the interplay of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. When demand for a currency exceeds supply, its value appreciates. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, its value depreciates.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting foreign exchange market meaning in business today.
Role of Central Banks, Conclusion for foreign exchange market project
Central banks play a significant role in managing exchange rates through monetary policy. They can intervene in the foreign exchange market to buy or sell their own currency, influencing its supply and demand.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting three participants in foreign exchange market today.
Forecasting Foreign Exchange Rates
Forecasting foreign exchange rates is a crucial aspect of international finance, enabling businesses, investors, and policymakers to make informed decisions. Various methods are employed to predict currency movements, each with its strengths and limitations.
Quantitative Forecasting Methods
- Technical Analysis: This method analyzes historical price data to identify patterns and trends that may predict future movements. It involves using charts, indicators, and mathematical formulas to identify potential trading opportunities.
- Econometric Models: These models use statistical techniques to analyze economic data, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, to forecast currency movements. They attempt to quantify the relationship between economic fundamentals and exchange rates.
- Time Series Analysis: This method uses statistical techniques to analyze historical time series data to identify patterns and trends that may help predict future movements. It involves techniques such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models.
Qualitative Forecasting Methods
- Expert Opinion: This method involves gathering insights from experts, such as economists, analysts, and market participants, to forecast currency movements. Experts rely on their knowledge, experience, and judgment to make predictions.
- News and Event Analysis: This method considers news events, political developments, and economic announcements that may impact currency movements. Analysts assess the potential impact of these events and incorporate them into their forecasts.
Challenges and Limitations
Forecasting currency movements is inherently challenging due to several factors, including:
- Market Volatility: Currency markets are highly volatile, making it difficult to predict short-term movements accurately.
- Unforeseen Events: Political instability, natural disasters, and other unforeseen events can significantly impact currency movements.
- Complexity of Economic Factors: A wide range of economic factors, both domestic and international, interact to influence exchange rates.
Successful and Unsuccessful Forecasting Techniques
The success of a forecasting technique depends on various factors, including the time horizon, market conditions, and the skill of the forecaster. Some examples of successful forecasting techniques include:
- Moving Averages: This simple but effective technique can help identify trends and support and resistance levels.
- Econometric Models: When economic fundamentals are stable, econometric models can provide accurate forecasts.
- Expert Opinion: Experienced analysts with a deep understanding of the market can provide valuable insights.
Conversely, some examples of unsuccessful forecasting techniques include:
- Technical Analysis: While technical analysis can be helpful for short-term trading, it is less reliable for long-term forecasting.
- News and Event Analysis: Relying solely on news events can lead to overreaction and poor forecasting outcomes.
- Linear Regression: This simple statistical model assumes a linear relationship between economic factors and exchange rates, which may not always be the case.
Risk Management in Foreign Exchange Trading

Engaging in foreign exchange trading involves a myriad of potential risks, necessitating the implementation of effective risk management strategies to safeguard capital and enhance trading outcomes. Understanding the various risks associated with forex trading and the techniques employed to mitigate these risks is crucial for traders and investors.
Investigate the pros of accepting (exhibit foreign exchange market) the supply of dollars curve slopes upwards because in your business strategies.
Identifying Foreign Exchange Trading Risks
- Currency Risk: Fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to losses if trades are not properly hedged.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can impact currency values and affect the profitability of trades.
- Liquidity Risk: Illiquid markets can make it difficult to enter or exit positions quickly, potentially leading to significant losses.
- Political Risk: Political events, such as elections or policy changes, can create market volatility and affect currency values.
- Counterparty Risk: Dealing with unreliable brokers or counterparties can expose traders to financial losses.
Strategies for Mitigating Foreign Exchange Trading Risks
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like forward contracts or options to offset the risk of adverse currency movements.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple currencies to reduce the impact of fluctuations in any single currency.
- Position Sizing: Managing the size of trades relative to available capital to limit potential losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting pre-determined levels at which trades are automatically closed to prevent excessive losses.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Calculating the potential reward for a trade in relation to the potential risk to ensure a favorable risk-to-reward profile.
Importance of Risk Management in Foreign Exchange Trading
Effective risk management is paramount for traders and investors in foreign exchange markets. By implementing sound risk management strategies, traders can:
- Protect their capital from significant losses.
- Enhance the profitability of their trades.
- Manage market volatility and uncertainty.
- Increase confidence in their trading decisions.
- Adhere to regulatory requirements and best practices.
Applications of Foreign Exchange Market: Conclusion For Foreign Exchange Market Project
The foreign exchange market plays a vital role in facilitating global economic activities, international trade, and investment. It provides the necessary platform for exchanging currencies, enabling businesses, individuals, and governments to engage in cross-border transactions seamlessly.
Furthermore, the foreign exchange market supports tourism and cross-border payments. When individuals travel to foreign countries, they need to exchange their home currency into the local currency to make purchases and pay for services. The foreign exchange market facilitates these currency conversions, ensuring that travelers have access to the local currency they need.
Businesses
- Import and Export: Businesses engaged in international trade use foreign exchange services to convert currencies when purchasing goods from or selling goods to foreign suppliers or customers.
- Cross-border Investments: Companies that invest in foreign markets need to exchange currencies to acquire assets, make investments, or raise capital in different countries.
- Hedging Currency Risks: Businesses with international operations use foreign exchange services to hedge against currency fluctuations, protecting themselves from potential losses due to exchange rate movements.
Individuals
- Overseas Travel: Individuals traveling abroad need to exchange their home currency into the local currency to cover expenses such as accommodation, transportation, and entertainment.
- Remittances: Foreign exchange services enable individuals to send money to family members or friends living in different countries, supporting cross-border financial flows.
- Currency Trading: Some individuals engage in currency trading as a form of investment or speculation, seeking to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates.
Recent Trends and Innovations in Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the emergence of new market participants. These trends and innovations are shaping the way currencies are traded and managed.
Technological Advancements
- Electronic Trading Platforms: Electronic communication networks (ECNs) and multi-dealer platforms (MDPs) have revolutionized currency trading, enabling faster execution and greater transparency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are used for data analysis, risk management, and automated trading, enhancing efficiency and decision-making.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain-based solutions offer secure and transparent cross-border payments, potentially reducing costs and settlement times.
New Market Participants and Trading Platforms
The foreign exchange market is seeing the entry of new players, including non-bank financial institutions, fintech companies, and retail investors. These participants are bringing diverse perspectives and innovative trading strategies to the market.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes, such as the Dodd-Frank Act in the US and the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) in the EU, have aimed to increase transparency and reduce risk in the foreign exchange market.
These trends and innovations are transforming the foreign exchange market, creating opportunities for participants and challenges for regulators. They will continue to shape the future of currency trading and global finance.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of the foreign exchange market is essential for thriving in the interconnected global economy. By leveraging the knowledge and strategies Artikeld in this project, individuals and organizations can effectively manage currency risks, optimize international transactions, and harness the power of foreign exchange to fuel their financial success.
